Made up of nitrogen and oxygen, compressed medical air is odorless, nonflammable, and free of particles, oil, moisture, and trace contaminants. In hospitals, dental offices, and other healthcare facilities, compressed air is supplied either through a medical gas pipeline system, which uses a compressor to manufacture and distribute filtered air, or through pressurized medical air cylinders. Where pipeline air supply systems are not feasible or available, medical air cylinders provide the compressed air needed for critical applications such as surgery, anesthesia, and respiratory support.
Let’s look at four of the most common uses for compressed medical air.
1. Carrying Agent For Inhaled Anesthetics
Used as a carrier gas to transport inhaled medications and anesthetic agents before and during surgical operations and medical procedures, compressed air offers a safe method for patients to receive anesthesia. Mixing medical air with an anesthetic agent helps control the administered dose, while keeping the patient comfortable and breathing normally through the procedure.
Anesthetic gas inhalation, mixed with nitrous oxide or medical air, is a reliable element of general anesthesia administration. Because of its lower oxygen content, medical air can be a safer anesthetic carrier gas than nitrous oxide, especially for patients sensitive to oxygen toxicity. Delicate cases of respiratory failure may require treatments with specific concentrations of medical air, to keep oxygen levels precise and controlled.

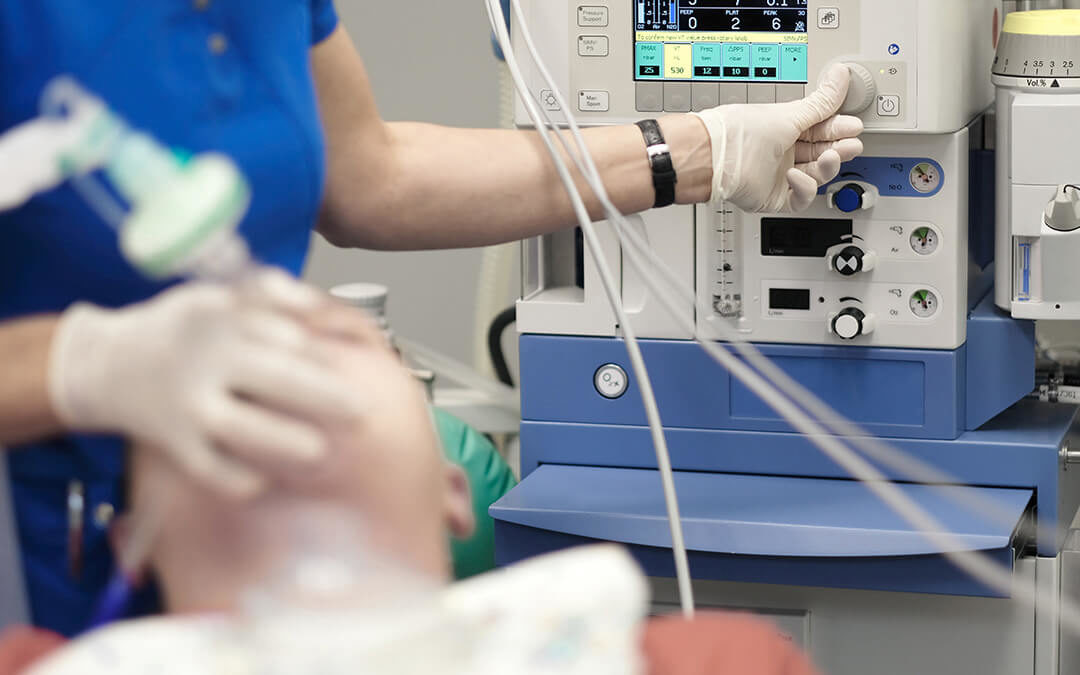
2. Breathing Assistance During Surgery
Doctors and health care professionals rely on medical air to help keep patients breathing comfortably in the operating room and in other critical care areas. Compressed medical air provides safe breathing air for patients under sedation, patients struggling to breathe on their own, and patients under treatment for varying respiratory conditions. A steady supply of medical air during an operation or procedure helps ensure steady breathing throughout.
3. Clean Air For Ventilators And Incubators
Ventilators and incubators must deliver a clean, controlled supply of compressed air, to ensure patient health and safety. Newborn babies, for example, need the cleanest air possible during their first hours of breathing – especially following any complications during birth. Medical breathing air must be free of even trace amounts of virus or bacteria.
Pressure-compensated flow control allows regulated distribution of medical air into ventilators, face masks, nebulizers, endotracheal tubes, hyperbaric chambers, and neonatal intensive care units (NICU) – to control the rate of administration, adjusted to individual patient needs. When breathing ambient air poses a health risk to the patient, medical air must be on hand to help maintain healthy respiratory function.
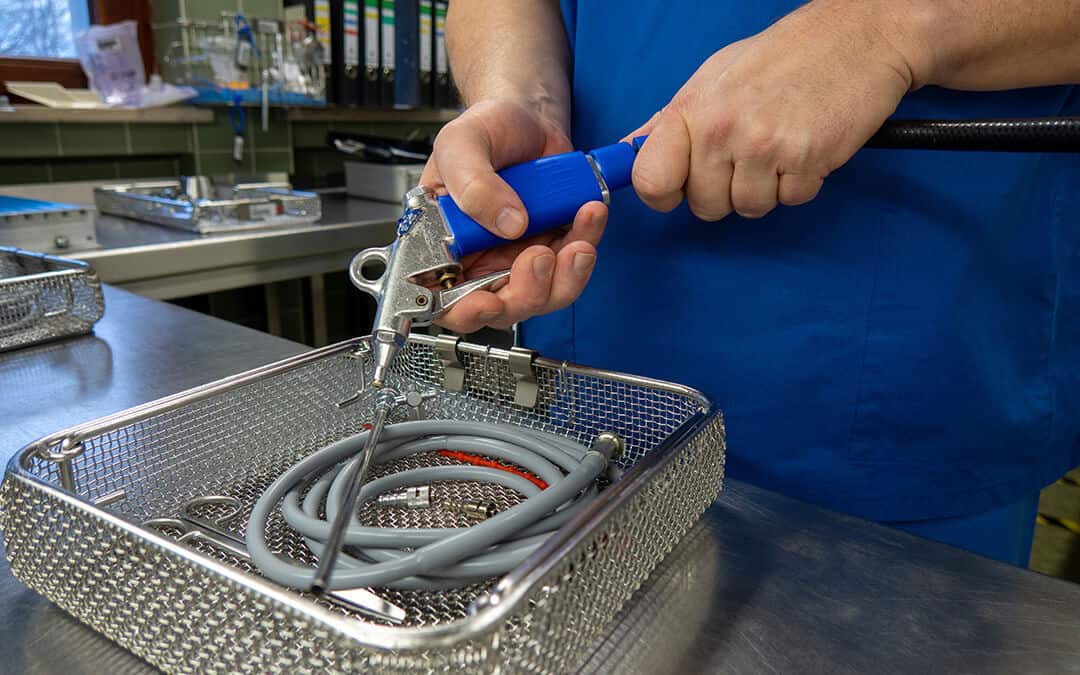
4. Operation Of Surgical Tools
Compressed air can be used as a contaminant-free power source for air-driven surgical tools in operating rooms, dentist chairs, and primary care medical facilities. Compressed air provides power to pneumatic instruments for puncturing, drilling, sawing, and other surgical procedures requiring precise air flow and even pressure.
Oral surgical instruments, orthopedic instruments, surgical saws and drills, handheld medical tools – compressed air can be used to power pneumatic medical equipment of all sorts – including tools and systems designed to clean and sterilize medical instruments. In laboratories, compressed air can power instruments used for blood analysis, oxygen and nitrogen generation, and other research activity.
The Versatility Of Medical Air
Compressed air offers uncontaminated, controlled air flow, to deliver breathable air to patients during medical and dental procedures, to treat patients with breathing issues and other respiratory deficiencies, and to deliver pneumatic power to surgical instruments.
Contact CalOx to learn more about the benefits medical compressed air can bring to medical practice.