Lasers have been used in dentistry since the 1960s to treat a variety of dental problems from pain to inflammation. And while these lasers have an FDA stamp of approval, the American Dental Association’s (ADA) Seal of Acceptance has yet to give them one. However, the ADA is cautiously optimistic about the role of laser technology in the field of dentistry since it provides some amazing benefits. Here’s a look at the innovative CO2 laser and how it’s used in dentistry the world over.
What Are CO2 Lasers?

In their essence, all lasers work by delivering energy in the form of light. With CO2 lasers, electricity is run through a gas-filled tube containing a mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen and helium. The active medium (in this case CO2 gas) is pumped with an electrical current, producing light that is guided by articulated arms or hollow waveguides to their desired source. The laser then acts as a cutting instrument or a vaporizer of tissue that it comes in contact with.
CO2 lasers are continuous-wave lasers, meaning they produce a steady output of 0,600 nm infrared wavelength. This unique wavelength lets them accurately cut and efficiently coagulate tissue, making CO2 lasers ideal for delicate dental procedures such as cutting tissue, biopsies and more. Recently, a hard-tissue-capable CO2 laser has become available, allowing for efficient cutting of enamel, dentin and bone.
CO2 Lasers in Dentistry
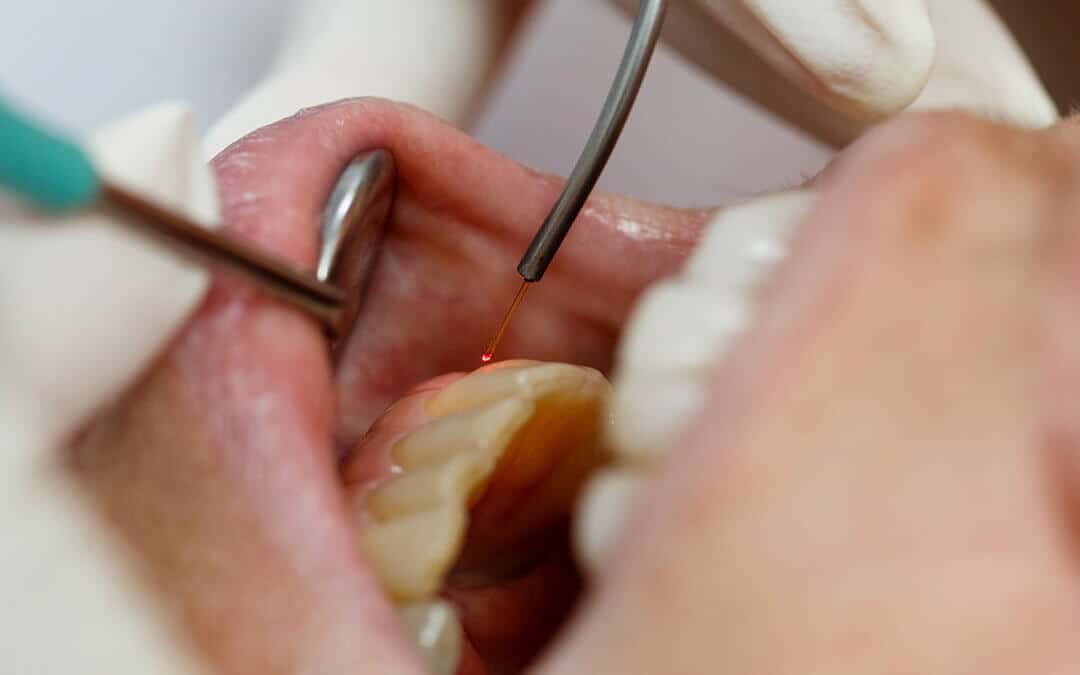
With their efficiency and safety, CO2 lasers help dentists perform a variety of procedures and treatments. CO2 lasers offer controlled thermal effects and sealing of nerve endings, allowing for a more comfortable and stable experience for the patient. When compared to traditional dental drills, CO2 lasers often cause less pain, reducing the need for anesthesia. They also minimize bleeding and swelling during soft-tissue treatments, leading to healthier teeth and gums. Additionally, CO2 lasers help reduce procedure length and can reduce or eliminate the need for sutures in many cases.
While there are some cons to CO2 laser use, such as minimal use in commonly performed dental procedures (like fillings) and their much more expensive cost ($600 for a standard drill vs. a few thousand dollars for the same procedure), the advantages of CO2 lasers far outweigh their disadvantages. When used correctly, CO2 lasers can provide successful treatment for:
- Gingivoplasty and gingivectomy
- Soft tissue, cysts and fibroma
- Ulcerous lesions, including aphthous ulcers
- Frenum release / frenectomy
- Abscesses (drainage)
- Flap surgery
- Biopsy (incisional & excisional)
- Excision & ablation of lesions, benign & malignant lesions, oral cavity tumors and hemangioma
- Salivary gland pathologies
- Pre-prosthetic gum preparation, leukoplakia
- Crown lengthening (soft tissue)
- Some tooth decay
- Gum disease
- Teeth whitening
- And more
While CO2 lasers come with a host of benefits for the patient, they also benefit the dentists who use them. With increased precision and power comes the increased productivity of dental practices. For example, since dentists can perform certain procedures more quickly due to the effectiveness of CO2 lasers, they can see more patients and help more people. If you’re a Southern California dentist who is interested in bringing CO2 lasers into your dental practice, CalOx can help you get there. CalOx is here to help you and your practice, just like we have been for over 80 years. Contact us today for your free quote!
Sources:
https://www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/ce-courses/ce394/co2-lasers
https://www.lightscalpel.com/laser-surgery/dental-laser/
https://sciencing.com/co-lasers-work-4899566.html